[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: NextBigFuture
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: Graphic
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: kathmandupost
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: kathmandupost
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: Yle
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: Graphic
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: NextBigFuture
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: Forbes
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: businessday
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: NDTV
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Sat, Jan 25th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: KLTV
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: ITV
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Forbes
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: CNET
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: YourTango
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: EKU
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: SHINE
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: WCJB
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Newsroom
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Forbes
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Townhall
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Techopedia
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Vanguard
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Bizcommunity
[ Fri, Jan 24th 2025 ]: Newsweek
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Forbes
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Yahoo
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Vanguard
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Newsweek
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Indiatimes
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: pna
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Forbes
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: WKRG
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: Firstpost
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: CIO
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: rnz
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: MSN
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: MSN
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: MSN
[ Thu, Jan 23rd 2025 ]: rnz
New technique to detect dark matter uses atomic clocks and lasers
 MSN
MSNA team of international researchers has developed an innovative approach to uncover the secrets of dark matter. In a collaboration between the University of Queensland, Australia, and Germany's metrology institute (Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt,
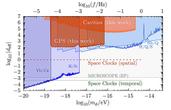
Read the Full MSN Article at:
[ https://www.msn.com/en-us/science/physics/new-technique-to-detect-dark-matter-uses-atomic-clocks-and-lasers/ar-AA1xNWHb ]
Similar Science and Technology Publications
[ Thu, Jan 16th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Thu, Jan 09th 2025 ]: MSN
[ Wed, Dec 18th 2024 ]: SciTech Daily
[ Tue, Dec 17th 2024 ]: Mashable
[ Mon, Dec 16th 2024 ]: Discover Magazine
[ Sun, Dec 15th 2024 ]: Daily Mail
[ Sun, Dec 15th 2024 ]: SciTech Daily
[ Tue, Dec 10th 2024 ]: SciTech Daily
[ Mon, Dec 09th 2024 ]: Scientific American
[ Mon, Dec 02nd 2024 ]: Tim Hastings
[ Sun, Dec 01st 2024 ]: Tim Hastings
[ Sun, Dec 01st 2024 ]: Tim Hastings
