White House Unveils Genesis Mission: A New Era of Cosmic Exploration




White House Announces the Genesis Mission: A New Era of Cosmic Exploration
On November 11, 2025, the Office of the President released a formal presidential action titled “Launching the Genesis Mission.” The directive signals a bold step forward in the United States’ commitment to planetary science, national security, and the global leadership of space exploration. By outlining a comprehensive plan to send a spacecraft to the far reaches of the inner solar system, the White House is reaffirming its dedication to the scientific discovery of the origins of life—and to securing the nation’s future in space.
1. The Genesis Mission at a Glance
Objective
The Genesis Mission is conceived as a sample‑return mission to a comet or near‑Earth asteroid, aimed at collecting pristine extraterrestrial material that could shed light on the chemical processes that gave rise to life on Earth. By returning dust grains and larger fragments to Earth for analysis, scientists hope to identify complex organic molecules, isotopic signatures, and the physical conditions that existed in the early solar system.
Scope
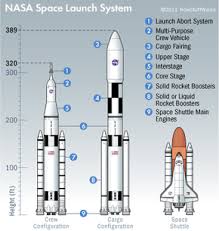
- Launch Vehicle: The White House action envisions collaboration with NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) or the United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V, depending on schedule and cost‑efficiency.
- Spacecraft: A modular design featuring a robotic lander, a sample‑collection arm, and a return capsule equipped with a heat shield for re‑entry.
- Target Body: The mission may focus on a near‑Earth comet such as 46P/Wirtanen or a small asteroid like 2019 QG, both of which can be approached within a feasible launch window.
- Timeline: The projected launch window opens in 2028, with a travel time of 3–4 years to the target, and an additional 1–2 years for return and recovery.
Budget
The action allocates $3.2 billion for the entire mission lifecycle—covering design, development, launch, operations, and Earth‑return analysis. Funding will be sourced from NASA’s Planetary Science Budget, a matching contribution from the Space Force for national security integration, and a public‑private partnership framework that encourages investment from companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and emerging aerospace startups.
2. Strategic Context
2.1 The White House Space Strategy
The Genesis Mission sits within the broader American Space Strategy, which emphasizes three pillars: (1) Science & Discovery, (2) National Security, and (3) Economic Growth. The presidential action references the 2025 Space Policy Framework, which reaffirms the United States’ role in ensuring planetary defense and fostering a thriving space economy.
2.2 National Security Integration
A notable feature of the action is the explicit partnership with the U.S. Space Force. By integrating planetary science assets with space situational awareness capabilities, the mission will provide real‑time data on asteroid trajectories, potential impact hazards, and resource mapping. The action cites the National Space Defense Plan and aligns with the National Strategy for Space-Based Earth Observation, underscoring how science missions can simultaneously bolster national defense.
2.3 International Collaboration
While the mission is a U.S.-led effort, the White House acknowledges the importance of global cooperation. Links in the action point to existing agreements with the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). These partnerships aim to share data, reduce duplication, and foster a unified approach to planetary protection.
3. Key Programmatic Elements
3.1 Scientific Heritage & Technological Readiness
The Genesis Mission builds upon the legacy of NASA’s 2001–2004 Genesis spacecraft, which collected solar‑wind samples. The new mission leverages advances in autonomous navigation, sample‑collection technology, and re‑entry heat‑shield design. White House notes that several of the required technologies are already in Technology Readiness Level (TRL) 6–7, significantly shortening the development timeline.
3.2 Planetary Protection & Ethics
The action references the Committee on Planetary Protection guidelines, ensuring that contamination protocols are strictly followed. The mission will employ sterilized instruments and a containment system designed to prevent forward contamination of the target body, thereby preserving the integrity of future astrobiological studies.
3.3 Public‑Private Partnerships
White House officials emphasize that the Genesis Mission will “ignite the commercial space sector” and “drive investment in high‑tech manufacturing.” The action includes a Commercial Space Exploration Initiative, which will provide tax incentives and procurement contracts for firms that contribute to mission hardware, software, or services.
4. Timeline & Milestones
| Phase | Milestone | Target Year |
|---|---|---|
| Concept Development | Final design review | 2026 |
| Technology Validation | TRL‑7 demonstration | 2027 |
| Launch | Launch vehicle and spacecraft deployment | 2028 |
| Target Encounter | Sample collection & return capsule release | 2030–2031 |
| Earth Return | Capsule re‑entry & recovery | 2032 |
| Data Analysis | Primary science results release | 2033–2034 |
5. Expected Outcomes
- Scientific Breakthroughs – Determining the isotopic ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen in cometary dust will refine models of how life‑bearing molecules arrived on Earth.
- National Security Gains – Real‑time monitoring of near‑Earth objects (NEOs) will improve impact prediction models, benefiting the Space Force’s Planetary Defense capabilities.
- Economic Impact – The mission’s high‑tech development will create jobs, stimulate the aerospace supply chain, and generate downstream innovations in robotics and data analytics.
- International Leadership – By leading a collaborative planetary science mission, the United States will strengthen diplomatic ties and set standards for future joint exploration efforts.
6. Additional Resources
The presidential action links to several foundational documents that provide deeper insight into the mission’s underpinnings:
- NASA’s Planetary Science Decadal Survey – outlines long‑term priorities for planetary exploration.
- U.S. Space Policy Framework (2025) – details the strategic vision for U.S. space activities.
- National Space Defense Plan – describes the integration of science assets into national defense.
- Committee on Planetary Protection Guidelines – outlines protocols for sample collection and contamination prevention.
These documents collectively frame the Genesis Mission as a multi‑disciplinary endeavor that advances scientific knowledge, protects national interests, and propels the U.S. to the forefront of the new space age.
7. Looking Forward
By officially launching the Genesis Mission, the White House has announced a tangible, high‑profile commitment to the next chapter of planetary science. The mission’s success will hinge on coordinated effort across federal agencies, industry partners, and international allies. Yet the potential payoff—an unprecedented glimpse into the cosmic origins of life—promises to reshape humanity’s understanding of our place in the universe. As the countdown begins, the United States stands ready to lead humanity on one of its most ambitious scientific quests yet.
Read the Full whitehouse.gov Article at:
[ https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/2025/11/launching-the-genesis-mission/ ]









































